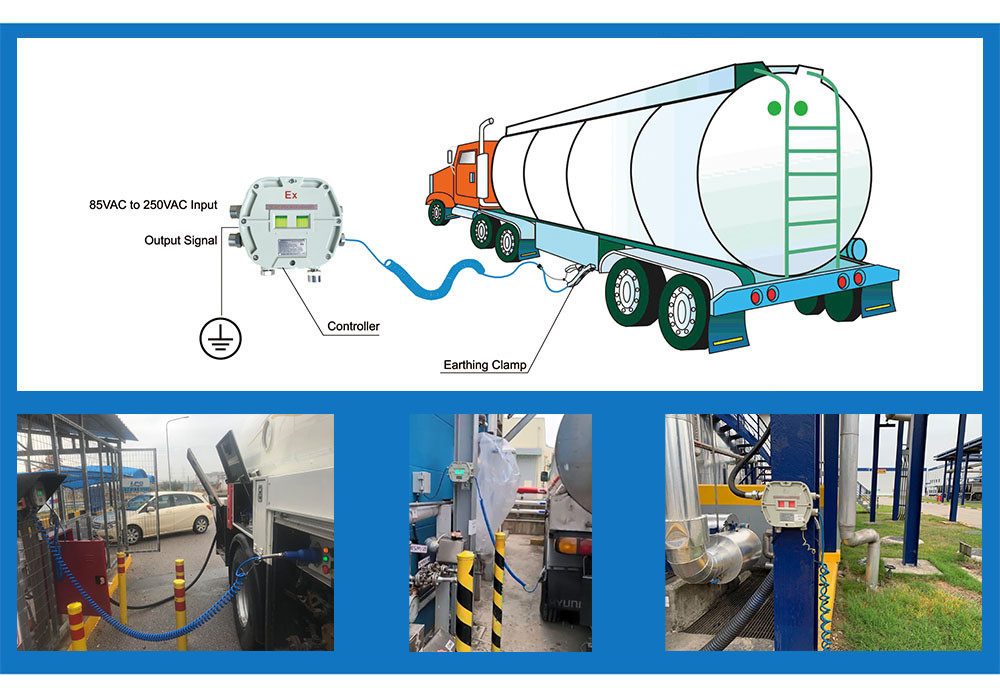
Application of Static Grounding Monitoring System
- Share
- publisher
- ALPTEC
- Issue Time
- Apr 26,2022
Summary
Application of Static Grounding Monitoring System
Legislation
concerning static electricity in hazardous area process industries
The ignition risk posed
by static electricity is addressed in European and North American legislation.
In the US, the Code of Federal Regulations that addresses hazardous location
activities, 29 CFR Part 1910 "Occupational Safety and Health
Standards", states that all ignition sources potentially present in
flammable atmospheres, including static electricity, shall be mitigated or
controlled.
In Europe, Annex II of
the ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU states the following:
Section: 1.3.2 Hazards
arising from static electricity: Electrostatic charges capable of resulting in
dangerous discharges must be prevented by means of appropriate measures so
"electrostatic discharges" are a known potential ignition source and
must be considered as part of the explosion risk assessment.
Safety
directives and function safety
Safety
directives
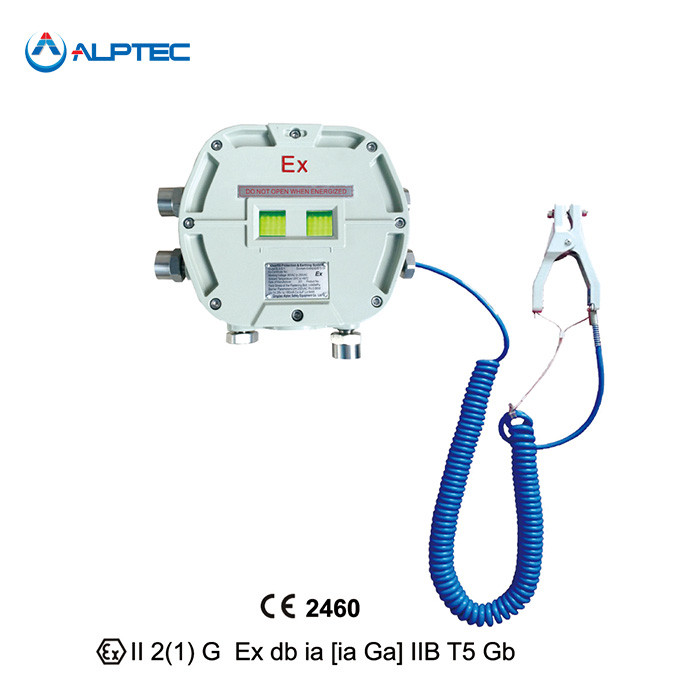
Anti-spill and
electrostatic grounding systems loaded on tank trucks shall comply with the ATEX
directives and standards. The system meets the general requirements of EN60079-0,
EN60079-1 and EN60079-11 for intrinsically safe circuit boards and electric
equipment.
ATEX specifies minimum
safety requirements for use in explosive atmospheres.
Its purpose is to
ensure that equipment such as oil spill sensors and control monitors do not
pose an ignition risk in an explosive atmosphere. ATEX does not assess the
safety function of the system, that is, its ability to detect liquid product
and stop the flow of product.
Function
Safety
Function safety
standards focus on the ability of a system to properly perform its safety
function, that is, to detect hazards and implement automatic protections to
ensure that in the event of a fault, the system fails in a predictable and safe
manner. Accredited functional safety bodies should carry out functional safety
certification to provide an unbiased assessment of the design and performance
of safety systems.
Operator
training
Every year in the
world, many oil depots and gas stations explode and catch fire due to improper
operation of operators. Therefore, it is essential to strengthen operator
training in flammable and explosive areas and should not be ignored. Operators
working in EX/HAZLOC areas should be trained in the basics of electrostatics!
They should be trained
on the intended function and proper use of grounding equipment and the use of
grounding equipment in accordance with company standard operating procedures.
For example, when loading and unloading oil into metal barrels, many operators
do not directly ground the metal barrels, and directly start the process of
paying and unloading oil. In this process, a large amount of static electricity
will be generated and cause accidents.
Operators should be
trained to avoid the following situations:
For example, if the grounding system and process interlocks have their ground connections removed from the process, thereby initiating an emergency shutdown process (e.g. switching down a pump), there may still be movement of material after the machine is stopped, thereby assuming the risk of continued electrostatic charge generation. If operators notice equipment has been changed or damaged (e.g. frayed cable connections), they should be encouraged to report the matter to the relevant personnel location (line manager, local maintenance staff) until someone who is able to use the equipment believes the equipment is safe and appropriate to use. Failure to provide training risks improper use of grounded equipment and/or failure to follow company standard procedures regarding static control.
Before the installation
of our equipment, we will provide professional guidance to the on-site
operators, and return visits regularly to supervise their normal operation.
Application
1. Road
tanker truck flammable
2. Filling,
mixing and blending of flammable/combustible materials in drums, portable
containers, mobile tanks and railcars.
3. Railway
loading and unloading, etc.